October 16, 2012 New Skeletal Augmentation through Protein Inhibition
Proteins are some of the most diverse structures in the biological system; they contribute for such a variety of purposes. Research at Georgia Health Sciences University (GHSU) has shown through trials on mice produces bone instead of fat. The drugs that were used to treat the specimen were for inflammatory diseases, whose side effect is bone degeneration. The protein, GILZ, was used to correct this factor because it manages fat production, ; the protein was then shut off because fat and bone pathways are complementary, if fat increase ceases then bone would have to increase, giving way for a new type of anti inflammatory that will save many from Osteoporosis.
Source: Science Daily
- Leave a comment
- Posted under Uncategorized
October 8, 2012 Artificial Skin for Halloween?
Researchers at Seoul National University have created a human-like membrane that is so sensitive that it can feel even the slightest quiver of motion. Its origin was from the signaling system found through-out the sensitive regions of the biological system. It is made up of polyurethane acrylate sheets that are meshed together and held through “Van der Waals Attractions.” The pressure sensing membrane is currently very affordable to make is being used as large area gauge sensors.
- Leave a comment
- Posted under Uncategorized
September 23, 2012 Painless way to administer Insulin.
Imagine if your ordinary inhaler could somehow help you keep your blood sugar in control. That’s exactly what is being tested at the Clinical trail at San Antonio Diabetics in Texas. Inhalers with a powder form of Insulin for Type 2 Diabetes are being used instead of using syringes. The other interesting fact is the it is “human’ Insulin, as claimed by endocrinologist, Sam Miller. He states the results of the trail are progressive and quite better than the previous product years ago.
- Leave a comment
- Posted under Uncategorized
September 16, 2012 Recycled Pacemakers can Save lives or Cause infections?
Researchers at the University of Pennsylvania have found a way to greatly help the economy and save hundreds of lives in third world countries. They are retrieving ICD’s and Pacemakers from cadavers after autopsies after learning that they still have battery left. Some of these devices can still last up to four years; for this reason, the FDA is trying to approve these devices for clinical testing prior to foreign shipment. There has been a study of improved health from the reuse of a pacemaker, however, this is quite a controversial issue due to the sterilization and has yet to be settled.
- Leave a comment
- Posted under Uncategorized
May 18, 2012 Obliterate Cancer from the Inside

Rice University Scientists are developing a way to effectively use chemotherapy to target cancer cells. This way, they can directly use bubbles bursts inside the body to break the cell barrier so the drugs can be administered – this results in a greater efficiency and a lower dosage will be required. This is clearly better than the conventional chemotherapy which covers a much broader spectrum of target surface area.
- Leave a comment
- Posted under Uncategorized
March 27, 2012 A blood test without bleeding

Myshkin Ingawale and his team from Biosense Technologies have come up for a solution that is a prick-free blood hemoglobin measurement device. This would heavily reduce pain and blood loss encountered when testing for hemoglobin. Designing the device was not easy, Ingawale tried 32 different designs before reaching an effective solution. The team at Biosense hopes this technology will be used in the developing world where cost and access is limited. It is always pleasing to see Biomedical Engineers improve and re-invent existing technologies to lower the cost, improve efficiency, and improve the design.
Source: TEDTalks
- Leave a comment
- Posted under Uncategorized
January 4, 2012 Hemophilia Patients Don’t Have To Bleed Anymore.
New Gene Therapy prevents bleeding in Hemophiliacs; the University College London Cancer Institute and St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital have successfully treated patients by injecting them with a clotting factor IX. This goes to the liver and lets it keep producing more. This was tested in trails where they checked the percentage in the patients, and it was shown to have increased 10%/year.
- Leave a comment
- Posted under Uncategorized
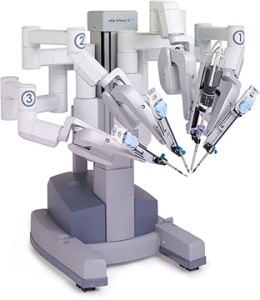
December 17, 2011 da Vinci Surgical Robots to Fix Satellites
The da Vinci robot which is currently used for surgeries is now being modified for use in space. The collaboration is between JHU, NASA, and WVU. They currently have managed to interface the da Vinci surgical robot’s console with an industrial robot 30 miles away, receiving 3D video and haptic feedback, while controlling its movements from afar. Current problems are with input lag, which is being improved on.
Source: JHU Gazette
- Leave a comment
- Posted under Uncategorized
November 2, 2011 Machines or just…Human Ingenuity
Kenichi Takahata of the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at the University of British Columbia is working on a “Medical Wonder!” A wireless implantable drug delivery device which is minutely small that its unnoticeable. In theory, It will deliver drugs in such perfect doses that it is said to cure cancer. He is also developing other mechanical implants that will vastly improve the medicinal world.
Source: The Globe and Mail
- Leave a comment
- Posted under Pharmacy
September 24, 2011 A Portable Brain Scanner that can fit in your pocket
Engineers at the Technical University of Denmark have created a neural monitoring system that works on the Nokia N900 smartphone. The phone provides power to the EEG headset. The headset monitors the electrical activity of the brain. They have bypassed the use of a normal PC, and made it possible with the Nokia smartphone. The application shows a 3d model of the brain and highlights regions where brain waves are detected, and there are additional analytical tools. This system provides a more portable, and cost effective solution of on the go EEG testing.
Source: NewScientist
- Leave a comment
- Posted under Uncategorized